-
Bespoke Software Development for Enterprise
We combine unique, tried and tested methodologies with a dedicated team to design, develop and deliver bespoke software to accelerate your Enterprise beyond what you thought possible.
Read more -
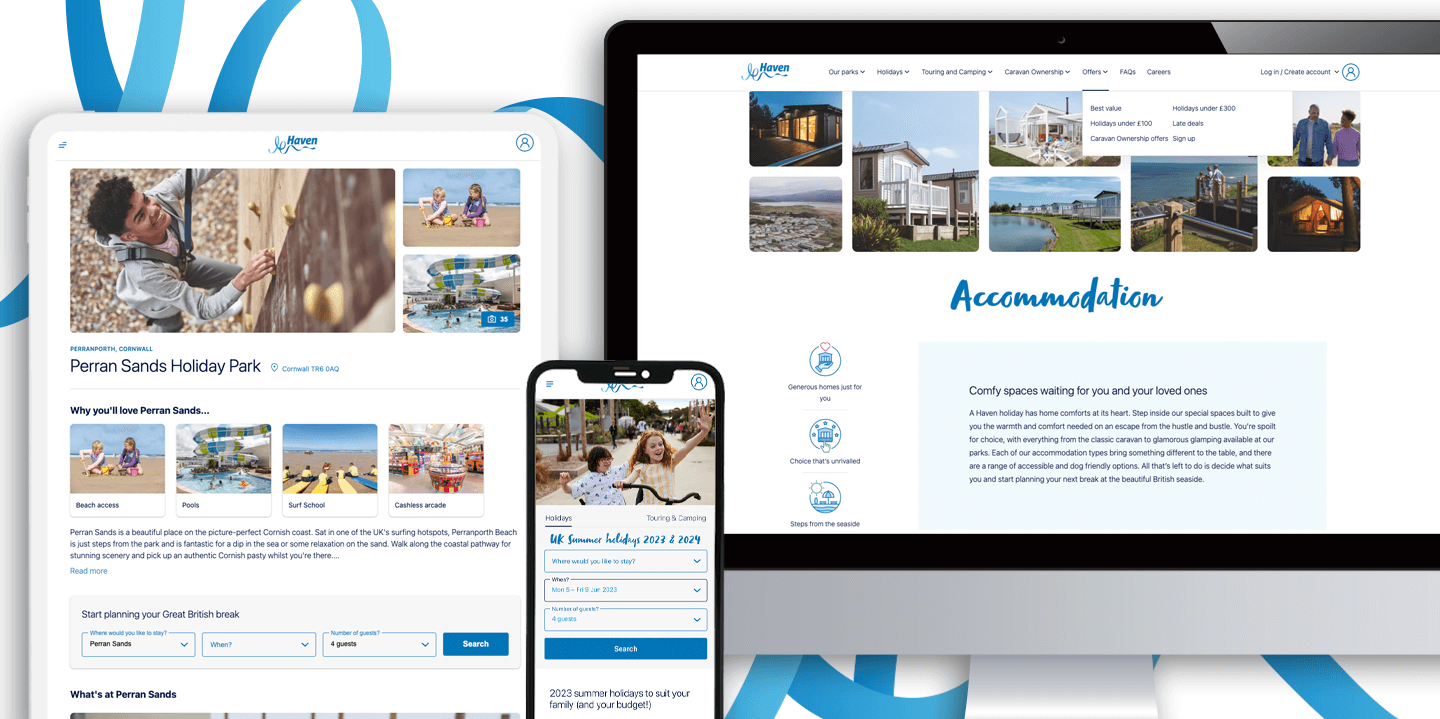
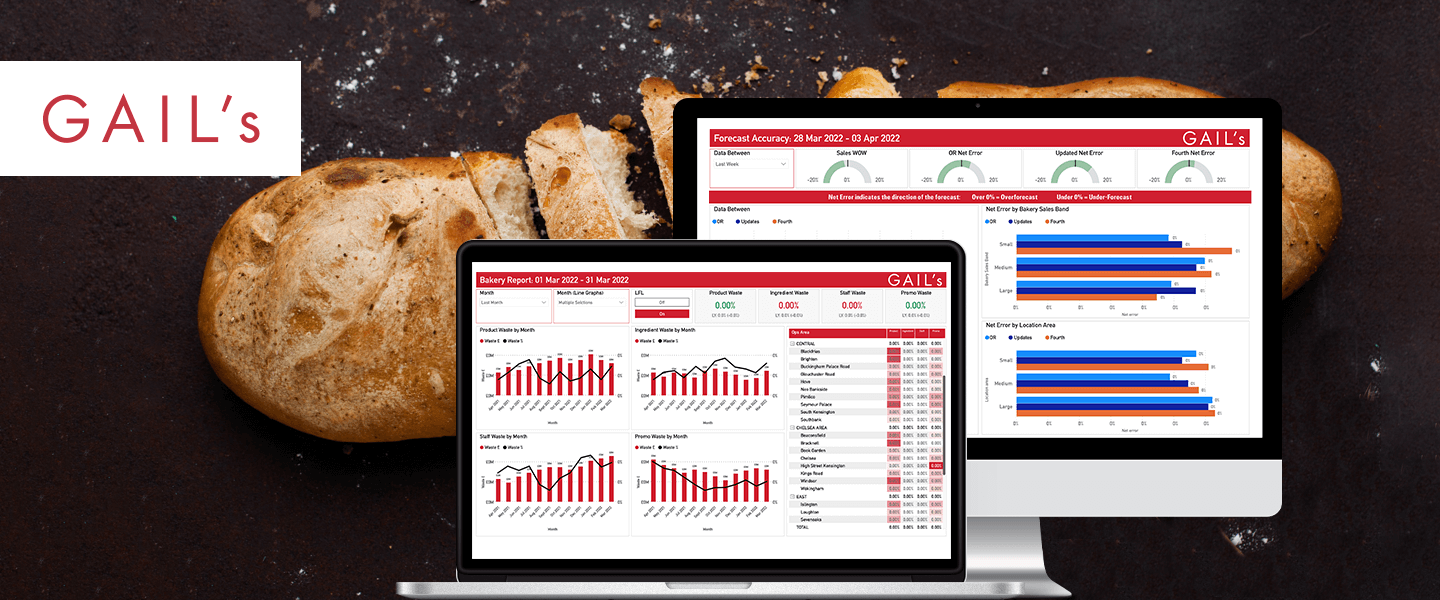
Product Development and SaaS for Established Businesses
We create products for organisations large and small across a variety of different sectors, including dedicated cloud solutions for multiple product verticals for licensing or resale.
Read more -
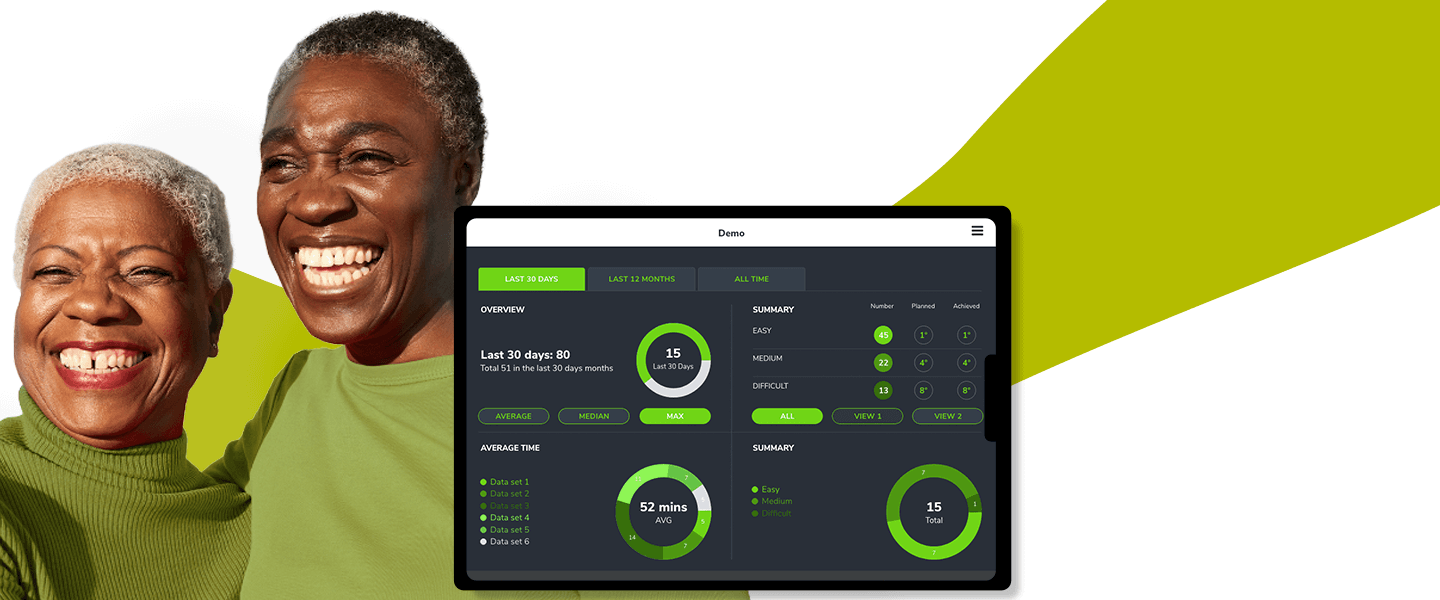
Bespoke Business Applications for SMEs
By leveraging One Beyond's Obelisk™ framework and with a bespoke approach for every business, we deliver web & mobile systems to accelerate your business.
Read more -
Software and Apps for Start-ups
One Beyond's Obelisk™ framework enables us to rapidly deliver competitively priced robust bespoke SaaS products and applications, with full code and IP ownership included.
Read more -
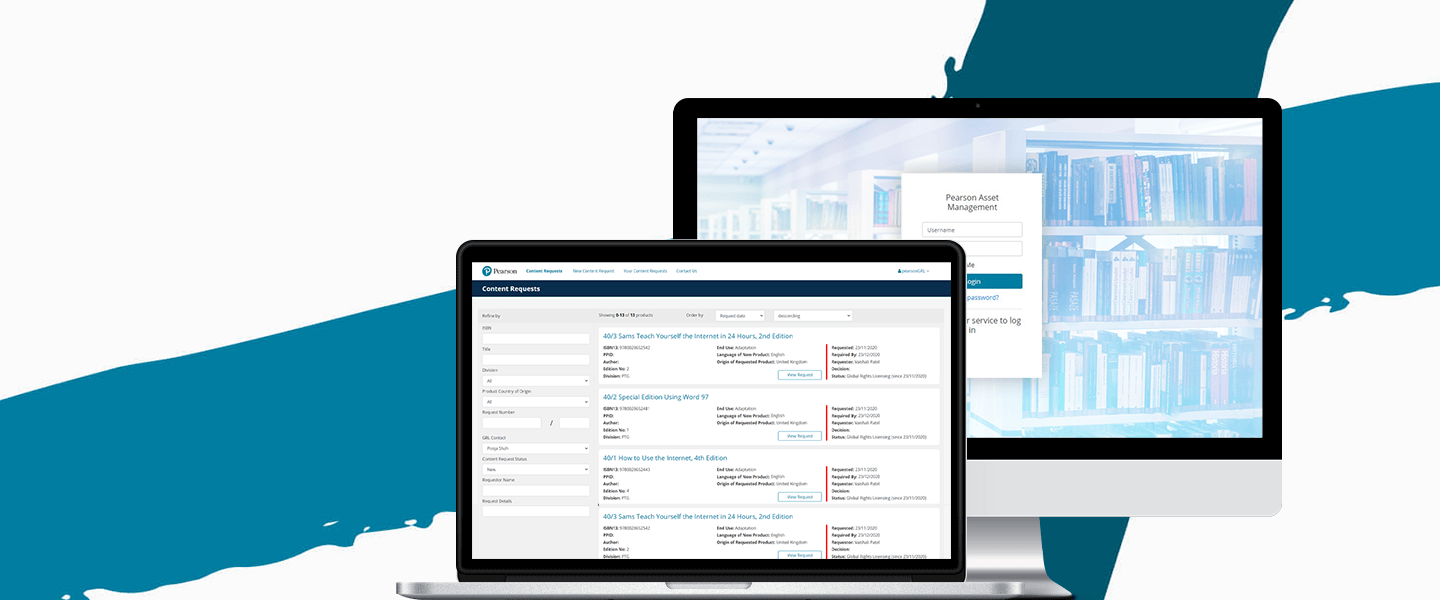
Software for Government and the Public Sector
One Beyond is an approved Crown Commercial Service supplier to the UK government with multiple reference projects, including the Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).
Read more

We will be with you every step of the way – from initial planning to delivery, and beyond.
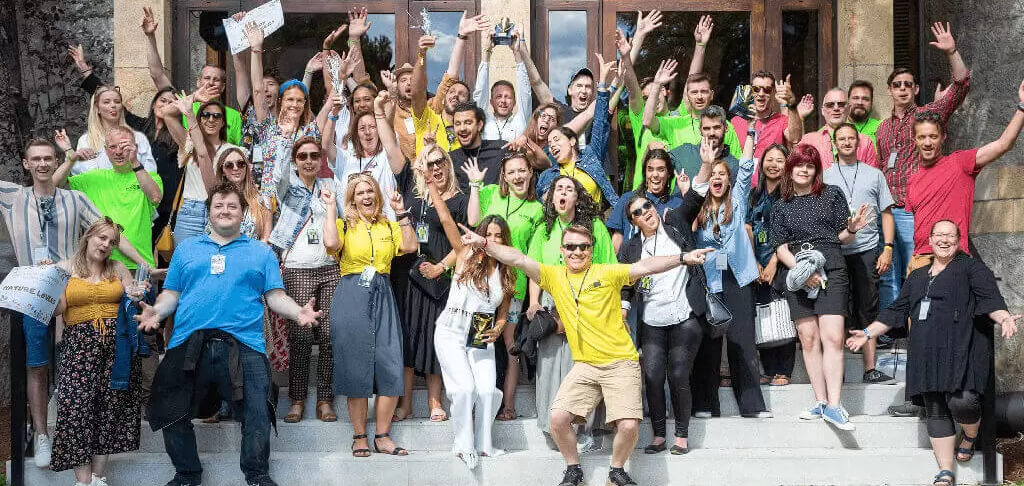
Our multi-award winning 200+ team of expert software developers create bespoke software products, apps and operational systems for SMEs, enterprise, not-for-profit, government and funded start-ups using a choice of Microsoft and Javascript technologies.
Case Studies
Companies that trust One Beyond.
Since 1994 the team at One Beyond has been developing bespoke software and we have established a reputation as a leading digital transformation partner. We help clients to automate, streamline and simplify their processes by delivering intuitive, cost-effective and scalable technology solutions.
Latest Blog Posts
Get in touch
We love to talk software development! Complete the form to speak to one of our friendly consultants based here in the UK for all your bespoke software development requirements.
Where to find us
Head Office
Victoria House, 50-58 Victoria Road, Farnborough, Hampshire, GU14 7PG
London
33 Glasshouse Street,
London, W1B 5DG
Or if you prefer, you can email us on [email protected]